Commercial Biomass Briquette Production: Waste to Profit Guide
Building a biomass briquetting plant might seem simple. Many see it as merely compressing waste material. However, truly successful businesses understand how to transform a production line into an efficient, sustainable value-creation system. This endeavor involves more than just purchasing a machine. It is about constructing a complex ecosystem of supply chains, chemical transformations, and market strategies. This guide delves into key aspects often overlooked, revealing critical insights for profitable and sustainable operations in the biomass fuel briquettes industry.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Market Prospects and Profit Margins for Biomass Fuel Briquettes?
- Which Agro-Forestry Wastes Are Suitable as Raw Materials? How Can Stable and Low-Cost Raw Material Supply Be Ensured?
- From Raw Material Collection to Finished Product, What Is the Complete Production Process for Biomass Fuel Briquettes?
- How to Choose the Most Suitable Briquetting Equipment and Auxiliary Machinery for Specific Capacities and Raw Materials?
- How to Ensure High Quality and Burning Efficiency of Biomass Briquettes to Meet Customer Needs?
- How Much Capital Is Needed to Invest in a Biomass Briquette Production Line? Where Are the Main Expenses?
- How Are Environmental Issues Handled and Compliance with Regulations Maintained During Briquette Production?
- Who Are the Main Buyers of Biomass Briquettes? How Can Sales Channels Be Efficiently Expanded?
- How to Choose a Reliable Equipment Supplier and Get Professional Project Solutions?
- FAQs
- Conclusion: Your Success in Biomass Briquetting
- About Durable
What Are the Market Prospects and Profit Margins for Biomass Fuel Briquettes?
The global demand for sustainable energy sources continues to grow. Biomass fuel briquettes offer a clean, renewable alternative to fossil fuels. This creates significant market prospects for businesses converting agro-forestry waste to fuel. Briquettes are widely used in industrial boilers, power generation, and residential heating. The market is driven by environmental regulations, increasing energy costs, and the abundant availability of biomass waste. Profit margins can be substantial, especially when raw material costs are managed effectively and production efficiency is high. Businesses can benefit from local waste streams and supply an energy product with a stable and growing demand.
The profitability of a biomass briquette business depends on several factors. These include raw material sourcing costs, the efficiency of the production line, energy consumption, and the selling price of the final product. Countries with policies promoting renewable energy often provide incentives, further enhancing profitability. For example, replacing coal with biomass briquettes in industrial settings can significantly reduce carbon footprints. This helps companies meet environmental targets while often providing a cost-effective fuel solution. The consistent quality and high energy density of well-produced briquettes make them attractive to various industrial and commercial buyers.
Which Agro-Forestry Wastes Are Suitable as Raw Materials? How Can Stable and Low-Cost Raw Material Supply Be Ensured?
A critical component of a successful biomass briquette plant is securing a stable and low-cost supply of suitable raw materials. A wide range of agro-forestry wastes can be utilized. These include wood sawdust, wood chips, agricultural straw (straw dryer), rice husks, peanut shells, cotton stalks, and other fibrous plant materials. The suitability of a raw material depends on its lignin content, moisture content, and availability. Materials with higher lignin content naturally bind better under pressure and heat.
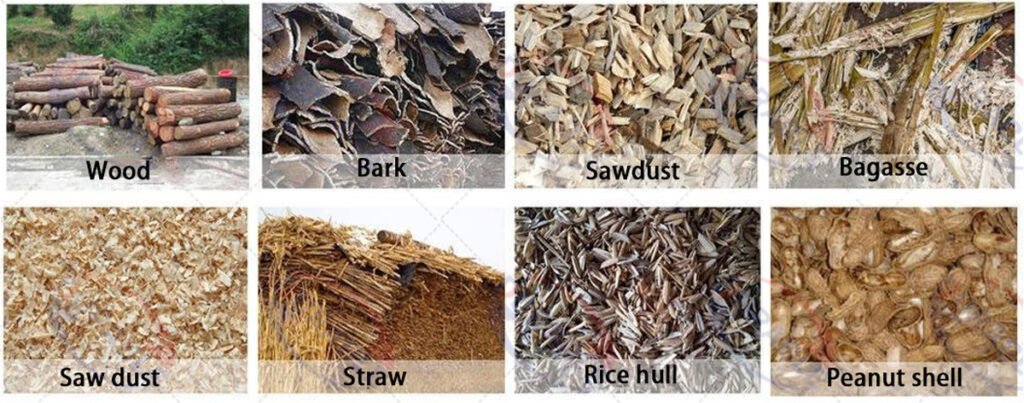

The actual cost of raw materials is a complex function, not simply the purchase price. Most new entrants focus solely on the unit purchase price, like “how much per ton of sawdust.” This often leads to significant losses in other areas. The true raw material cost equals (purchase price + transportation cost + pre-treatment cost + potential loss cost + inventory management cost) divided by the effective dry matter weight converted into qualified briquettes. The biggest variables and hidden costs are moisture content and impurities. For instance, purchasing sawdust with 50% moisture content at 100 RMB per ton and sawdust with 20% moisture content at 120 RMB per ton may seem like a straightforward comparison. However, 50% moisture sawdust, dried to 10% moisture, yields only about 0.56 tons of dry matter per wet ton. This means the raw material cost per ton of dry matter is 100 / 0.56 = 178.57 RMB, not including drying energy consumption, equipment wear, and transportation. Conversely, 20% moisture sawdust, dried to 10% moisture, yields about 0.89 tons of dry matter per wet ton. The raw material cost per ton of dry matter is 120 / 0.89 = 134.83 RMB. Establishing strict raw material acceptance standards and using testing equipment, such as moisture testers, is essential. Prioritizing nearby, low-moisture, low-impurity, and stable-supply raw materials is recommended. Collaborating long-term with large wood processing plants or farms can help control quality and costs at the source.
From Raw Material Collection to Finished Product, What Is the Complete Production Process for Biomass Fuel Briquettes?
The biomass briquetting production line involves several key stages, each crucial for the quality and efficiency of the final product. Understanding this complete process is vital for optimizing operations.
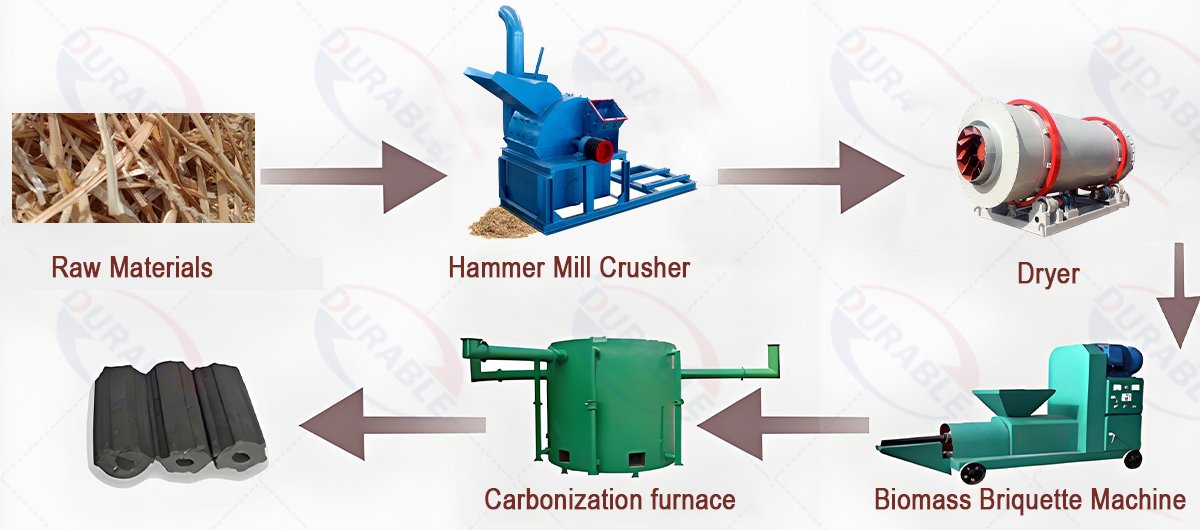
- Raw Material Collection and Storage: Raw materials are collected from various sources. They are then stored in a covered area to prevent moisture absorption and contamination. Efficient storage reduces handling costs.
- Crushing: Large biomass materials like wood branches or agricultural stalks need to be reduced in size. A biomass crusher or hammer mill crusher breaks them down into smaller particles, typically 3-5mm. This prepares the material for drying and pressing.
- Drying: The moisture content of the crushed biomass must be precisely controlled. It needs to be between 8% and 12% for optimal briquetting. A biomass dryer or sawdust dryer is used for this step. The dryer should ensure uniform moisture removal. Many consider the dryer a simple dewatering device, believing that merely removing water is sufficient. However, the dryer is more accurately a “uniformity reactor.” Briquette formation is not simple physical extrusion. It relies on the lignin in biomass materials softening under high temperature and pressure, then re-solidifying as a natural binder. This process requires precise and strict control over the raw material’s moisture content, typically between 8% and 12%. If the material is too dry, lignin activity is insufficient, resulting in loose briquettes. If it is too wet, briquettes may expand, crack, or even fail to form. An unstable drying process can lead to significant variations in briquette quality, frequent clogging and increased wear on the briquetting machine, and even fire risks. A well-designed drying system’s core task is to uniformly adjust incoming material with varying moisture levels to the optimal moisture content required by the briquetting machine. Investing in a dryer with good temperature and residence time control, such as a triple pass rotary drum dryer or an airflow dryer (for different raw materials), ensures uniform heating and minimal moisture gradients. Additionally, integrating waste heat from the briquetting machine or other factory processes into the drying system can achieve energy cascading, significantly reducing operating costs.
- Briquetting: The dried and crushed biomass is fed into a briquetting machine. High pressure and temperature, without any artificial binders, compress the material into dense briquettes. This process activates the natural lignin in the biomass, which acts as a glue.
- Cooling: Freshly pressed briquettes are hot and relatively soft. They need to be cooled to ambient temperature to harden and stabilize their shape. This prevents cracking and expansion.
- Packaging: Cooled briquettes are then packaged, usually in bags or bulk, for storage and transportation. Proper packaging protects them from moisture.
How to Choose the Most Suitable Briquetting Equipment and Auxiliary Machinery for Specific Capacities and Raw Materials?
Selecting the right equipment is paramount for the success of a biomass briquette business. This involves choosing the main briquetting machine and all auxiliary machinery. The choice depends on the type of raw material, desired output capacity, and the specific characteristics of the briquettes needed for the target market.
There are primarily two types of briquetting machines:
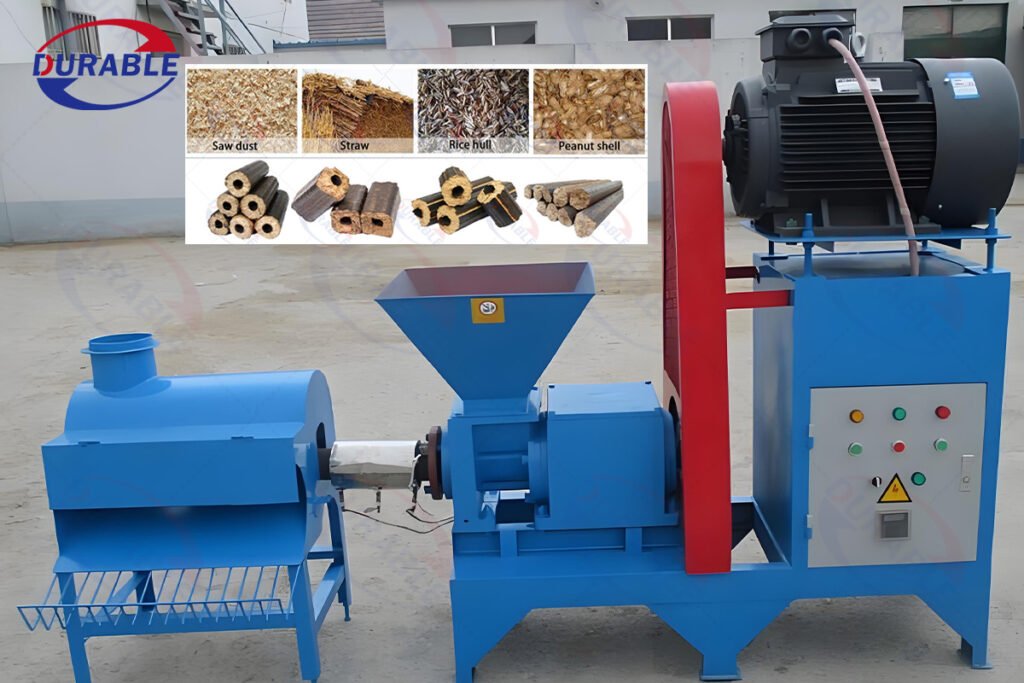


- Screw Press Briquette Machines (also known as rod making machines): These machines use a large screw to compress biomass, often producing briquettes with a hole in the center. They typically produce high-density briquettes. The rod making machine from Durable is suitable for this.
- Ring Die Pellet Mills: While often used for smaller pellets, industrial versions can produce larger briquettes. These machines are known for high output and consistent product quality.
When purchasing a briquetting machine, customers often focus on the initial price and hourly output. However, the true production cost is heavily influenced by the wear parts, such as dies and rollers. These components operate under extreme pressure and friction, leading to significant wear. The hardness and abrasiveness of the raw material, along with moisture content fluctuations, greatly affect their lifespan. The cost of wear parts can account for 20% to 40% of the total production cost, sometimes even exceeding electricity consumption. Many equipment suppliers do not explicitly detail the lifespan and replacement costs of these wear parts in their quotes. Before purchasing, it is crucial to inquire about the material, expected lifespan (based on specific raw materials and moisture content), and replacement price of wear parts. Understanding if parts can be repaired or re-ground is also beneficial. During production, strict inventory management and replacement schedules for wear parts should be established. More critically, investing in wear part lifecycle management, such as learning hardfacing techniques or seeking professional wear part repair services, is advisable. High-performance wear-resistant alloys like high-chromium alloy steel or tungsten carbide coatings can significantly extend lifespan, though their initial cost is higher and requires careful consideration.
How to Ensure High Quality and Burning Efficiency of Biomass Briquettes to Meet Customer Needs?
Ensuring high quality and burning efficiency is crucial for the market acceptance and success of biomass fuel briquettes. Briquettes are not a generic product; they are “engineered fuel.” Different application scenarios demand specific characteristics in terms of density, calorific value, ash content, size, shape, and durability. Many producers mistakenly believe all biomass briquettes are the same, producing first and then seeking a market. This approach can lead to products that do not meet specific market demands.
For example, industrial boilers prioritize stable calorific value and ash melting point. Size can be large, and shape is less critical. Home fireplaces and stoves require long burning times, low ash content, and clean, smokeless combustion. Size and shape need to be convenient for storage and loading. Biomass power plants focus on large-scale supply and precise ash control. Export markets may have extremely strict standards for density, moisture content, and packaging. Therefore, before investing in a production line, thoroughly research the target market. Understand the specific fuel requirements of potential buyers. This research directly influences the choice of briquetting machine type (screw presses generally produce denser briquettes, while ring dies offer more consistent quality), briquette size and shape (e.g., some markets prefer cylindrical, others block-shaped), and even whether subsequent carbonization is needed. The goal is not to create a “one-size-all” product, but a tailored solution for specific market needs. Consistent quality starts with uniform raw material preparation, especially moisture content control. The briquetting machine’s pressure and temperature settings also play a role. Higher density briquettes burn longer and have higher energy density. Low ash content and high calorific value are key indicators of quality. Regular testing of these parameters is essential.
How Much Capital Is Needed to Invest in a Biomass Briquette Production Line? Where Are the Main Expenses?
Investing in a biomass briquette production line requires significant capital. Understanding the major expenses helps in accurate budgeting and financial planning for a biomass energy investment. The total cost varies widely depending on the desired capacity, level of automation, and chosen equipment quality.
Main capital expenditure areas include:
- Land and Infrastructure: Cost for the factory site, foundations, and necessary buildings. This can be a major expense, especially in urban or industrial areas.
- Raw Material Pre-processing Equipment: This includes crushers like hammer mill crushers, dryers such as triple pass rotary drum dryers or wood chips dryers, and conveyors. These are essential for preparing raw materials.
- Briquetting Machines: The core of the production line. The cost of a briquetting machine or pellet making machine depends on its type (screw press, ring die), capacity, and manufacturer.
- Cooling and Packaging Systems: Equipment for cooling briquettes and packaging them for sale.
- Environmental Control Systems: Dust collection, and potentially flue gas treatment systems.
- Installation and Commissioning: Costs associated with setting up the equipment and getting the plant operational.
- Working Capital: Funds for initial raw material purchases, utilities, labor, and maintenance until the business generates consistent revenue.
Initial investment for a medium-scale plant (e.g., 1-2 tons/hour) can range from hundreds of thousands to several million dollars, not including land costs. For example, a quality biomass crusher and dryer might cost a significant portion of the total. A comprehensive financial plan is necessary.
How Are Environmental Issues Handled and Compliance with Regulations Maintained During Briquette Production?
Environmental compliance is a critical aspect of biomass briquetting production. Proper management of emissions and waste is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for the long-term sustainability and public image of the business. Dust management in biomass briquette production is not just an environmental concern; it is a “profit center” and a “lifeline.” Many factories view dust as an unavoidable byproduct, often only using simple collection bags.
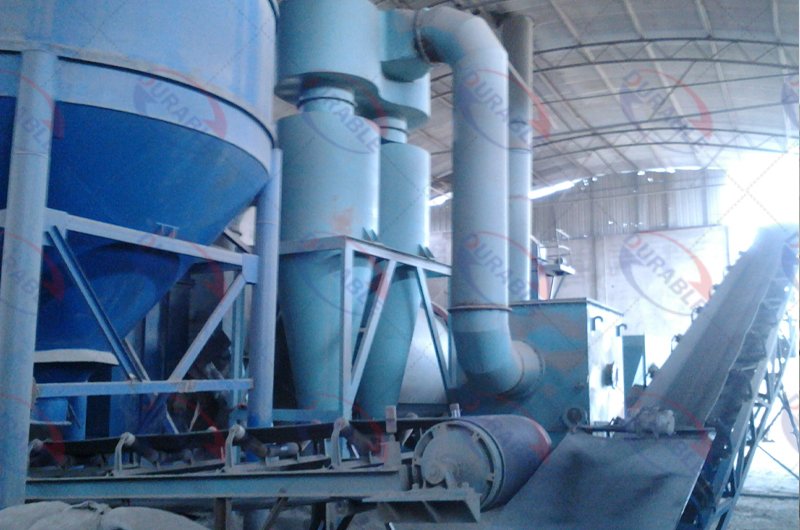


Biomass dust, especially wood dust, is highly flammable and explosive. At certain concentrations in the air, it can easily cause dust explosions when exposed to an open flame or static electricity. This represents not only significant property loss but also a major risk of injury or death. Furthermore, dust is a valuable raw material; allowing it to dissipate is a loss of profit. For safety, it is mandatory to invest in professional dust collection systems (cyclone separators + bag filters) to ensure that the dust concentration in the production environment remains below explosive limits. Fire and explosion prevention measures, such as explosion-proof fans, explosion vents, and spark detection and suppression systems, are essential. For efficiency, collected dust should be recycled back into the crusher or briquetting machine as supplemental raw material. High-pressure briquetting machines efficiently utilize fine dust. This not only increases output and reduces waste but also mitigates environmental pollution. Dust management is therefore an investment in employee safety, compliance with national regulations, and an effective means of increasing raw material utilization and profit. Consulting professional industrial dust removal companies from the design stage to integrate dust control into the production line planning is highly recommended.
Who Are the Main Buyers of Biomass Briquettes? How Can Sales Channels Be Efficiently Expanded?
Understanding the target market is key to efficiently expanding sales channels for biomass fuel briquettes. The main buyers fall into several categories, each with distinct needs and purchasing behaviors.



- Industrial Boiler Owners: Factories and industrial facilities using boilers for steam generation or process heating are major consumers. They often seek a consistent, high-energy-density fuel to replace coal or natural gas.
- Power Plants: Some power plants, especially those converting from coal, use biomass briquettes as a co-firing fuel or dedicated biomass fuel. They require large, stable supplies.
- Residential and Commercial Heating: Households, hotels, restaurants, and other commercial establishments use briquettes for heating, cooking, or in fireplaces. These buyers often prioritize clean burning, low ash, and convenient packaging.
- Agricultural Sector: In some regions, briquettes are used for crop drying or in agricultural processing.
- Export Markets: Developed countries with strict environmental regulations and high energy costs are often willing to import high-quality biomass briquettes. This offers significant opportunities for expansion.
Efficiently expanding sales channels involves direct sales to industrial clients, establishing distribution networks for residential markets, and engaging in bulk supply agreements with larger entities. Participating in energy trade shows and online B2B platforms can also connect producers with potential buyers. Tailoring the product to specific market requirements, as discussed earlier, significantly aids market penetration.
How to Choose a Reliable Equipment Supplier and Get Professional Project Solutions?
Choosing a reliable equipment supplier is one of the most critical decisions for a biomass briquette business. The long-term success and profitability of the plant heavily depend on the quality, reliability, and support provided by the supplier. Many customers, when selecting equipment, compare prices and choose what seems like the best-performing crusher, dryer, or briquetting machine from different manufacturers.
However, a briquette production line is an organic whole. Even if individual machines perform excellently, if they are not compatible with each other, the overall system efficiency will be severely compromised. The seamless connection between equipment, buffering, and consistency of the control system determine the production line’s stability, automation level, and ultimate profit margin. Purchasing equipment from multiple suppliers may seem to reduce individual machine costs. However, this often leads to:
- Connection issues: Different equipment inlet/outlet sizes and heights may not match, requiring additional modifications.
- Incompatible control systems: This necessitates developing additional interfaces or separate operations, increasing labor and failure rates.
- Difficult fault tracing: When problems arise, suppliers may shift blame, making diagnosis and resolution challenging.
- Complex spare parts management: Multiple brands mean maintaining several spare parts inventories.
Therefore, it is advisable to seek suppliers capable of providing complete solutions. Even if the individual machine price is slightly higher, but its provided system integration, automation level, unified after-sales service, and spare parts system, can save significant hidden costs and management effort in the long run. A smooth, automated production line can substantially reduce labor costs, enhance operational efficiency, and improve safety. When budgets allow, opting for branded, integrated solutions is an essential path toward large-scale, industrialized production. A reliable supplier offers not just machines, but a professional project solution. This includes technical consultation, plant design, equipment customization, installation supervision, operator training, and after-sales support. Look for suppliers with proven track records, extensive industry experience, and positive customer testimonials. A supplier that understands the entire production process and can offer a tailored solution is more valuable than one simply offering low-priced machines. Durable provides comprehensive solutions for biomass fuel briquette production, ensuring integrated systems and robust support.
FAQs
Question 1: What is the typical return on investment (ROI) for a biomass briquette plant?
The ROI for a biomass briquette plant can vary significantly. Factors include raw material cost, electricity rates, and market prices for briquettes. Generally, well-managed plants can achieve an ROI within 2-4 years, especially with optimized raw material sourcing and efficient operations.
Question 2: Are there any specific certifications required for biomass briquettes?
Yes, depending on the target market, certifications may be required. For example, in Europe, standards like ENplus or DINplus ensure briquette quality. Meeting these standards can significantly enhance market access and pricing.
Question 3: Do I need to add binders when making biomass briquettes from waste?
For most fibrous biomass waste, no artificial binders are needed. The natural lignin present in the biomass acts as a binding agent. It softens under high pressure and temperature during briquetting, holding the particles together.
Question 4: How should biomass raw materials be stored effectively?
Raw materials for biomass briquettes should be stored in a dry, covered area to prevent moisture absorption. Good ventilation is important to avoid mold growth. Proper storage reduces material loss and maintains quality before processing.
Question 5: What are the main industrial applications for biomass briquettes?
Biomass briquettes are widely used as fuel in industrial boilers for steam generation, process heating, and electricity production in biomass power plants. They replace fossil fuels like coal, offering a cleaner and more sustainable energy source.
Question 6: How can the production of biomass briquettes contribute to environmental sustainability?
Producing biomass fuel briquettes turns agricultural and forestry waste into valuable energy, reducing landfill waste and deforestation. It offers a carbon-neutral energy source, as the CO2 released during combustion is recaptured by growing new biomass.
Conclusion: Your Success in Biomass Briquetting
Success in the biomass briquette business transcends mere machinery acquisition. It involves a holistic understanding of raw material sourcing, the precise control of the production process, and a keen awareness of market demands. By treating briquettes as engineered fuel and optimizing every step from waste to a marketable energy product, businesses can unlock substantial profits. Focusing on system integration, proactive maintenance, and rigorous quality control leads to a robust, sustainable, and highly profitable venture. The transformation of agro-forestry waste to fuel offers a compelling opportunity for environmental stewardship and economic growth.
About Durable
Durable, established in 2001, is a leading Chinese manufacturer specializing in mineral processing equipment and construction machinery. We leverage our extensive experience in high-temperature industrial processing and material handling to engineer and build complete, integrated biomass briquetting production lines. Our solutions are designed for efficiency, reliability, and environmental compliance. We understand that every project is unique. Our team collaborates closely with clients to design systems perfectly tailored to specific raw materials, desired output capacities, and business goals. From initial technical consultation and plant design to equipment customization, installation supervision, operator training, and comprehensive after-sales support, Durable ensures that each investment translates into a successful and sustainable operation.
For expert guidance and a customized project proposal for your biomass briquette plant, contact Durable’s engineering team today.
 Durable Machinery
Durable Machinery