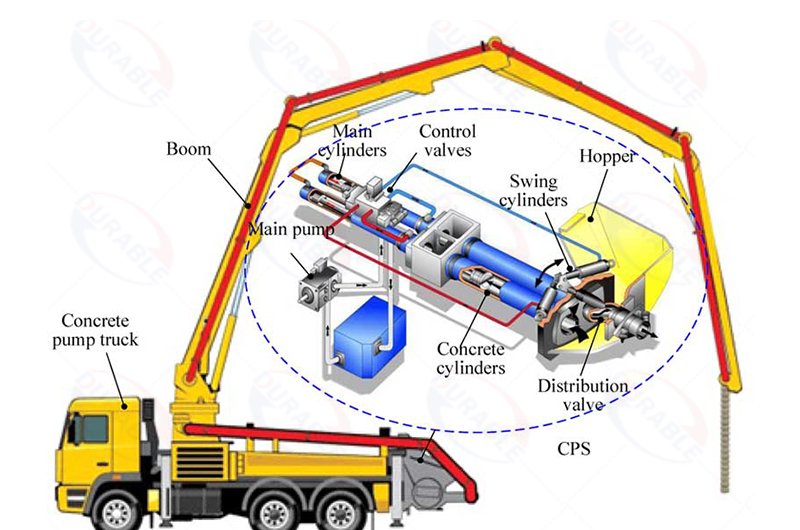
Concrete Pump Maintenance Tips: A Complete Guide
Effective concrete pump maintenance is crucial for construction projects. It directly impacts project timelines and overall profitability. Proper upkeep ensures equipment reliability. It also prevents costly breakdowns. This guide outlines essential practices for maintaining concrete pumps. Implementing these methods helps boost equipment performance. It also helps lower operational costs. Consistent attention to maintenance secures long-term investment value for you.

Table of Contents
- What is the importance of daily concrete pump maintenance?
- What are the key checks before starting a concrete pump?
- How does concrete pump cleaning affect equipment lifespan?
- How can one prevent and diagnose hydraulic system faults?
- How does one inspect and replace concrete pump wear parts?
- What are the special care requirements for concrete pumps in winter or long storage?
- How does one troubleshoot concrete pump operational anomalies?
- How does one plan for regular deep inspections and service cycles?
- How does comprehensive maintenance boost concrete pump asset value and ROI?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Summary and Recommendations
- About Durable
What is the importance of daily concrete pump maintenance?
Daily concrete pump maintenance forms the foundation of reliable operation. It ensures the equipment functions at peak efficiency. Neglecting these routine tasks leads to various problems for you. These issues include unexpected breakdowns and reduced pumping capacity. Such failures cause significant project delays. They also increase labor costs due to downtime. Consistent daily checks identify minor issues before they escalate. Early detection often allows for simple, inexpensive fixes. This prevents major component damage for your pump.
A robust preventative maintenance plan extends the service life of a concrete pump. It helps preserve the pump’s asset value. Properly maintained equipment experiences less wear and tear. This reduces the frequency and cost of major repairs. Regular maintenance also ensures the pump meets safety standards. This protects operators and other site personnel. Consistent concrete pump upkeep directly translates into higher uptime. It also means lower operating expenses. This directly contributes to a project’s profitability and schedule adherence. It is an investment for your operations.
Practical Tips for Operators
- Create a Checklist: Use a physical checklist for every pre-operation inspection. This ensures no step is missed.
- Document Findings: Record any issues found, no matter how small. This helps track potential problems over time.
- Report Immediately: Inform supervisors of any significant concerns. Quick action prevents bigger problems.
What are the key checks before starting a concrete pump?
Performing specific checks before each operation is vital for concrete pump safe operation. These pre-start inspections prevent accidents. They also ensure optimal pumping performance for you. First, verify all fluid levels. This includes hydraulic oil, engine oil, and coolant. Low fluid levels can cause severe damage to critical components. Next, inspect all hoses and pipelines. Look for kinks, leaks, or blockages. Damaged hoses can burst under pressure. This creates a significant safety hazard.
Inspect the structural integrity of the boom. Check for any cracks or deformation. Ensure all pins and locking mechanisms are secure. Verify that safety features, such as emergency stops, are functional. Test the remote control system for responsiveness. Check tire pressure and lug nut tightness for mobile units. For concrete trailer pumps and boom pumps, ensure outriggers deploy correctly and securely. These checks identify potential hazards or operational issues. Addressing them before starting prevents costly repairs and ensures personnel safety. This systematic approach minimizes risks and maximizes your operational readiness.
Essential Pre-Start Inspection Points
- Hydraulic Oil Level: Confirm it is within the manufacturer’s recommended range.
- Engine Oil & Coolant: Check for adequate levels to prevent overheating or engine damage.
- Hoses & Connections: Visually inspect for leaks, kinks, or signs of wear.
- Safety Switches: Test emergency stop buttons and safety interlocks.
- Boom Structure: Look for visible damage, loose bolts, or worn pins.
How does concrete pump cleaning affect equipment lifespan?
Thorough concrete pump cleaning is essential for extending equipment lifespan. Concrete is corrosive and hardens rapidly. Residual concrete left in the pump or pipelines causes significant issues. Internally, hardened concrete reduces pumping efficiency. It increases wear on critical components. These components include the S-tube, wear plates, and delivery cylinders. Buildup can restrict flow. It also causes pressure fluctuations and premature wear. This leads to costly repairs and reduced performance.
External cleaning removes dirt, dust, and concrete splatter. This prevents corrosion of metal parts. It also keeps control panels and gauges legible. Cleaning after each use is best. This prevents concrete from curing inside the system. Methods often involve flushing with water. Sometimes, a cleaning ball or sponge is pushed through the pipes. Proper cleaning prevents blockages. It maintains optimal flow characteristics. This directly contributes to the pump’s longevity. It ensures consistent, high-quality operation for you. It is a fundamental part of concrete pump upkeep.
Effective Cleaning Techniques
- Flushing with Water: After each pour, flush the system with water until it runs clear. This is the most common method.
- Cleaning Balls/Sponges: Push a cleaning ball or sponge through the delivery line using water or air pressure. This helps remove stubborn residue.
- High-Pressure Washing: Use a pressure washer for external cleaning. This removes spilled concrete and dirt from the pump body.
- Hopper Scraper: Manually scrape any hardened concrete from the hopper and agitator blades.
How can one prevent and diagnose hydraulic system faults?
The hydraulic system is the heart of a concrete pump. Its reliable operation is paramount. Preventing faults involves diligent hydraulic system maintenance. Regular checks of hydraulic fluid quality and level are critical. Contaminated fluid or low levels lead to overheating. This causes increased wear on pumps, motors, and valves. Replace hydraulic filters according to manufacturer guidelines. Clogged filters restrict flow. This starves components of necessary lubrication and cooling. Inspect hydraulic hoses and fittings for leaks. Leaks indicate potential system pressure loss and contamination ingress.
Diagnosing faults often involves monitoring pressure gauges and listening for unusual noises. A sudden drop in pressure might suggest a pump failure. It could also indicate a valve issue or a significant leak. Unusual whining or grinding sounds often point to cavitation. It could also mean pump wear. Overheating hydraulic fluid indicates a cooling system problem. It might also signal excessive system resistance. Addressing these symptoms promptly prevents minor issues from becoming catastrophic failures. This ensures the pump’s continued reliable operation and prevents expensive concrete pump repair methods.
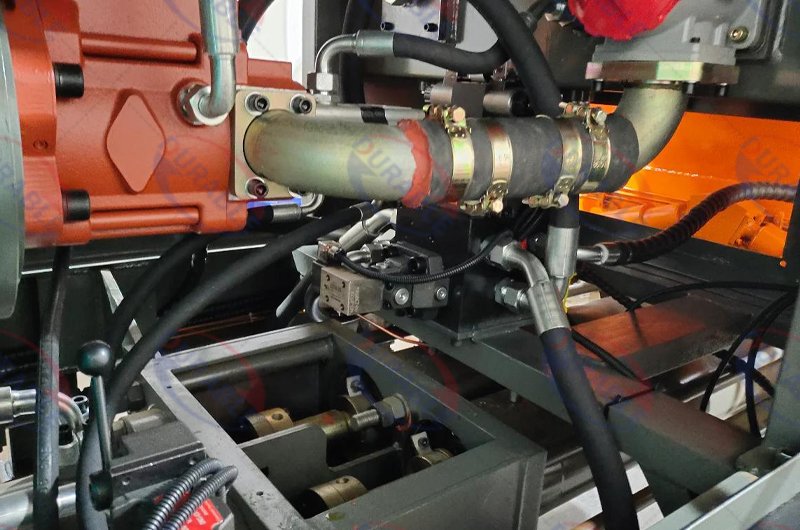


Common Hydraulic System Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Probable Cause | Solution | Your Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overheating | Low fluid, clogged filter, poor cooler | Check fluid, replace filter, clean cooler | Prevents component damage, extends fluid life |
| Loss of Power | Low fluid, pump wear, valve malfunction | Check fluid, inspect pump/valves | Restores full pumping capacity |
| Unusual Noise | Cavitation, worn pump, trapped air | Check fluid level, bleed air, inspect pump | Prevents further wear, ensures smooth operation |
| Fluid Leaks | Damaged hoses, loose fittings, worn seals | Replace hoses, tighten fittings, replace seals | Maintains pressure, prevents contamination |
[Understanding the basics of hydraulic system maintenance can also benefit other equipment like self-loading concrete mixers.]
How does one inspect and replace concrete pump wear parts?
Concrete pumps operate under immense pressure. They handle abrasive materials. This means certain components experience significant wear. Regular inspection and timely replacement of wear parts replacement are crucial for maintaining efficiency. Key wear parts include delivery pipes, S-tube, wear plates, cutting rings, and piston cups. Inspect delivery pipes for internal wear. This includes thinning of the pipe walls. Also look for external damage. Worn pipes can burst, posing a serious safety risk. Pump pipe replacement is necessary when wall thickness falls below safe limits.
The S-tube, wear plates, and cutting rings form the main pumping mechanism. Inspect these for excessive grooves or chips. These indicate reduced sealing efficiency. This causes material bypass and lower output. Piston cups inside the concrete cylinders wear down over time. Worn cups lead to concrete leakage past the piston. This reduces pumping efficiency and can damage the cylinders. Establish a schedule for inspecting these components. Replace them proactively. This prevents catastrophic failure during operation. Such proactive measures are central to effective concrete pump repair methods.
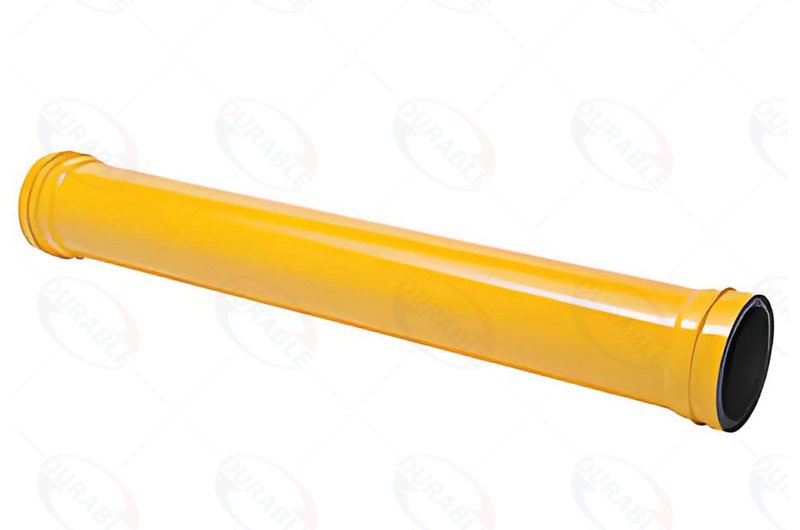
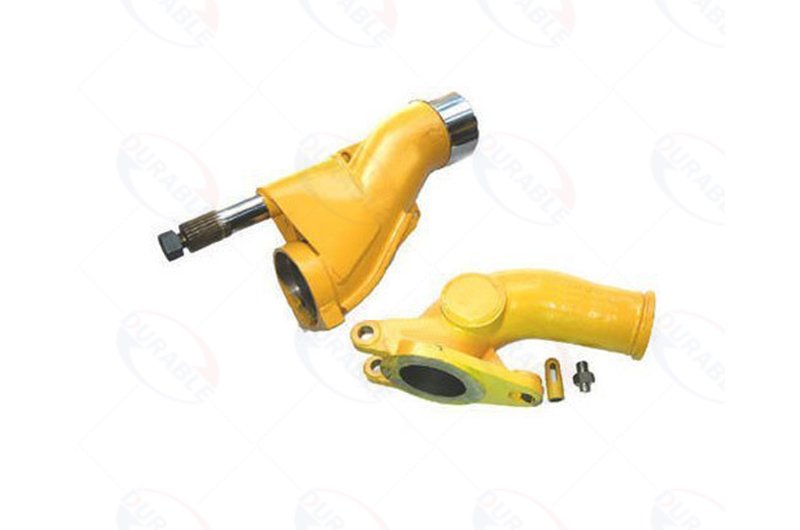
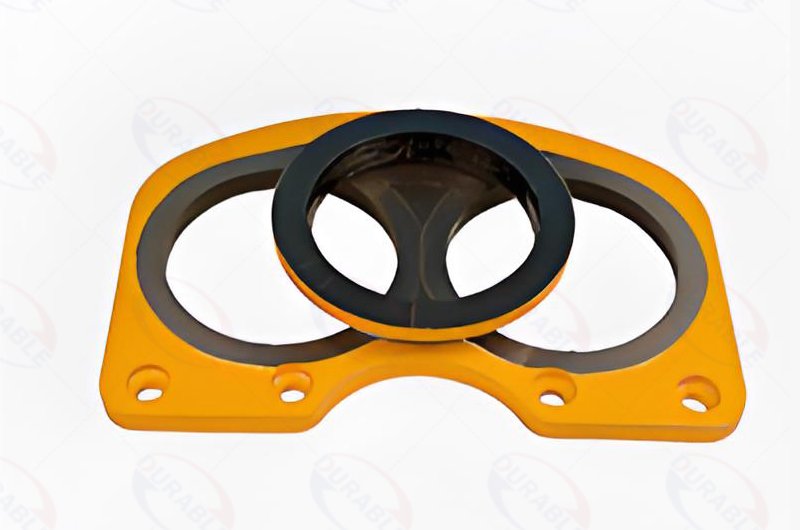
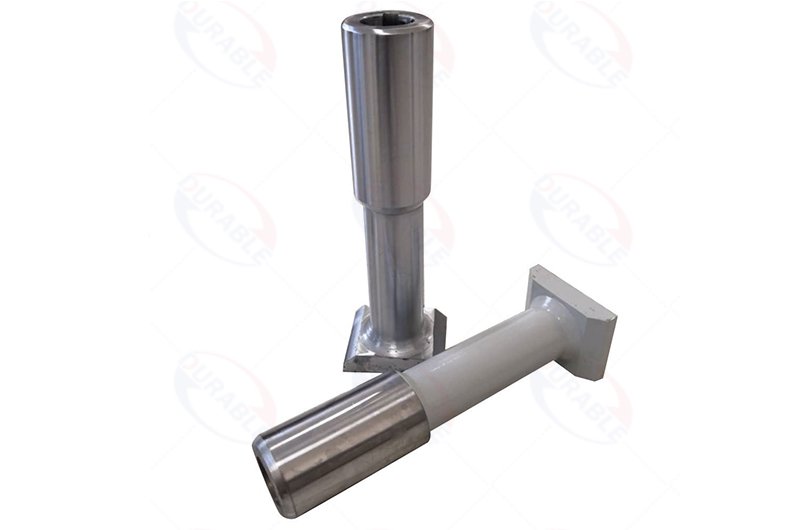




Critical Wear Parts to Monitor
- Delivery Pipes: Check regularly for thinning or blockages.
- S-Tube/Gate Valve: Inspect for wear, especially at the material flow path.
- Wear Plates and Cutting Rings: Look for grooves or chips that reduce sealing.
- Piston Cups: Examine for cracks, hardening, or signs of concrete bypass.
- Agitator Blades: Check for wear that reduces mixing efficiency in the hopper.
What are the special care requirements for concrete pumps in winter or long storage?
Equipment downtime maintenance for concrete pumps requires specific attention, especially during winter or extended storage. Freezing temperatures pose significant risks. Water left in the system can freeze and expand. This causes pipes, pumps, and valves to crack. Completely drain all water from the pump and pipelines. Use compressed air to ensure no residual water remains. Add antifreeze to the cooling system if the pump has a combustion engine. Check and charge the battery. Cold weather significantly reduces battery performance.
For long-term storage, additional steps are necessary. Thoroughly clean the entire machine, inside and out. Apply anti-corrosion grease or paint to exposed metal surfaces. Lubricate all moving parts according to the manufacturer’s manual. Store the pump in a dry, covered area. This protects it from direct weather exposure. Cover the exhaust and air intake. This prevents pests from nesting. Regularly check fluid levels during storage. Occasionally rotate mechanical parts. This prevents seizing. These measures prevent degradation and ensure the pump remains ready for service. They are vital for you to extend concrete pump lifespan.
Winterizing Your Concrete Pump
- Drain All Water: Ensure the water tank, cooling system, and flush out system are completely empty. Use compressed air.
- Antifreeze: Add appropriate antifreeze to engine cooling systems.
- Battery Care: Disconnect and store batteries in a warm place. Keep them charged.
- Fuel System: Fill the fuel tank to prevent condensation if storing for short periods. Add fuel stabilizer for longer storage.
- Protect Exposed Parts: Apply rust preventative to unpainted metal surfaces.
How does one troubleshoot concrete pump operational anomalies?
Operational anomalies, such as unusual noises or unstable pressure, demand prompt investigation. Effective concrete pump troubleshooting identifies the root cause. This prevents further damage. An unusual grinding or squealing noise often points to bearing failure. It could also mean insufficient lubrication in the S-tube. A high-pitched whine from the hydraulic pump suggests cavitation. This means it is starving for fluid. Check hydraulic fluid level and filter condition immediately.
Unstable pumping pressure or inconsistent flow indicates a blockage. It might also mean worn wear parts. Inspect the delivery line for obstructions. Check the condition of the wear plate and cutting ring. Low pumping output, despite normal engine speed, could mean worn piston cups. It could also mean air entering the hydraulic system. Systematically checking each potential failure point leads to quick diagnosis. This allows for timely concrete pump repair methods. Proper diagnosis minimizes downtime and reduces your repair costs. Operators should be trained to recognize these common symptoms.
Common Anomalies and Immediate Actions
- Excessive Vibration: Check for unbalanced components, loose connections, or structural damage.
- Concrete Not Pumping: Verify material consistency, check for blockages, or inspect wear parts for severe wear.
- Engine Stalling/Rough Running: Check fuel level, fuel filters, air filters, and engine oil.
- Boom Drift: Inspect hydraulic cylinders for leaks, check holding valves, or adjust boom settings.
How does one plan for regular deep inspections and service cycles?
Planning regular deep inspections and service cycles optimizes concrete pump performance optimization. This moves beyond daily checks. It involves comprehensive examinations by qualified technicians. Such inspections typically occur every few hundred operating hours. Or they occur annually. The schedule depends on usage and manufacturer recommendations. These cycles include thorough hydraulic system inspection. This covers pressure tests, fluid analysis, and valve checks. They also involve detailed structural integrity assessments. This means checking the boom for fatigue cracks.
Components like the gearboxes, axles, and engine receive dedicated attention. Lubrication points are serviced. All electrical connections are verified. This preventative maintenance plan identifies potential failures. It addresses them before they impact operations. It ensures the pump complies with all safety regulations. A detailed service history helps track wear rates. It also helps predict future maintenance needs. This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime. It extends your equipment’s economic life. This planning is crucial for long-term reliability.
Key Elements of a Service Schedule
- Hour-Based Servicing: Follow manufacturer’s recommendations for 250-hour, 500-hour, and 1000-hour intervals.
- Fluid Analysis: Regularly test hydraulic oil and engine oil for contaminants. This provides early warning of wear.
- Structural Integrity Checks: Use non-destructive testing (NDT) for critical stress points. This detects hairline cracks.
- Calibration: Recalibrate sensors and control systems for accurate operation.
How does comprehensive maintenance boost concrete pump asset value and ROI?
Comprehensive concrete pump maintenance directly boosts its asset value enhancement. It also increases the overall return on investment (ROI). Well-maintained equipment commands a higher resale value. Buyers prefer machines with a documented service history. This indicates reliability and care. Regular maintenance also reduces the pump’s depreciation rate. It extends its usable life. This means the initial investment spreads over a longer period. This improves cost-effectiveness.
Reduced breakdowns mean less unplanned downtime. This increases productivity. It also avoids costly rush repairs and project delays. Fuel efficiency often improves with well-maintained engines and hydraulic systems. This lowers daily operating expenses. Lower operating expenses, combined with extended equipment life, significantly enhance your ROI. This systematic approach transforms maintenance from a necessary cost into a strategic investment. It ensures the concrete pump remains a profitable asset throughout its operational life. This makes it a smart business decision for you.
Long-Term Benefits of Strategic Maintenance
- Higher Resale Value: Documented maintenance records demonstrate care. This increases your equipment’s value.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Fewer repairs, better fuel efficiency, and extended component life save money.
- Increased Uptime: Planned maintenance minimizes unexpected breakdowns and keeps projects on schedule.
- Enhanced Safety: Well-maintained equipment operates more safely. This reduces accident risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: How often should hydraulic fluid be changed in a concrete pump?
Hydraulic fluid change intervals depend on usage and fluid type. Typically, it is every 1000-2000 operating hours. Always follow the manufacturer’s specific recommendations. Fluid analysis can also help determine the optimal change interval.
Question 2: What are common signs of a blockage in a concrete pump pipeline?
Common signs include unstable pumping pressure, reduced flow rate, and increased engine strain. The pump may also make unusual noises. Check the delivery line, especially at bends, for obstructions.
Question 3: Is it better to perform maintenance in-house or outsource it?
This depends on internal expertise and resources. Routine daily checks are typically in-house. Major service cycles or complex concrete pump repair methods often benefit from specialized technicians. Outsourcing can be cost-effective for complex issues.
Summary and Recommendations
Effective concrete pump maintenance is a strategic imperative for any construction project. It ensures optimal equipment performance and significantly lowers operating costs. Daily checks, thorough cleaning, and diligent care for hydraulic systems and wear parts extend the pump’s lifespan. Special attention to winterization and storage practices prevents degradation. Proactive concrete pump troubleshooting and regular deep inspections minimize downtime for you.
Implementing a robust preventative maintenance plan boosts asset value and enhances overall return on investment (ROI). Such practices improve safety, efficiency, and project profitability. Durable Machine offers a comprehensive range of high-quality concrete pumps, including concrete boom pumps and concrete mixer pumps. Durable also provides guidance on their proper care. To discuss specific maintenance needs or to inquire about new equipment, contact Durable’s sales team today.
About Durable
Durable Machine, established in 2001, is a professional Chinese manufacturer. It specializes in B2B construction and mineral processing equipment. Based in Zhengzhou, the company focuses on the research, development, and production of robust machinery. This includes a wide range of concrete equipment. Examples are concrete boom pumps, concrete trailer pumps, and self-loading concrete mixers. State-of-the-art facilities and stringent quality control measures ensure complete customer satisfaction. Durable proudly exports its high-performance products to over 120 countries. It offers factory-direct solutions for diverse global construction needs.
 Durable Machinery
Durable Machinery